What is AI?
AI, also known as Artificial intelligence, is a technology with human-like problem-solving capabilities. AI in action appears to simulate human intelligence—it can recognize images, write poems, and make data-based predictions.
Modern organizations collect large data volumes from diverse sources, such as smart sensors, human-generated content, monitoring tools, and system logs. Artificial intelligence technologies analyze the data and use it to assist business operations effectively. For example, AI technology can respond to human conversations in customer support, create original images and text for marketing, and make smart suggestions for analytics.
Ultimately, artificial intelligence is about making software smarter for customized user interactions and complex problem-solving.

What are some types of AI technologies?
AI apps and technologies have increased exponentially in the last few years. Below are some examples of common AI technologies you may have encountered.
History of AI
In his 1950 paper, "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," Alan Turing considered whether machines could think. In this paper, Turing first coined the term artificial intelligence and presented it as a theoretical and philosophical concept. However, AI, as we know it today, is the result of the collective effort of many scientists and engineers over several decades.
1940-1980
In 1943, Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts proposed a model of artificial neurons, laying the foundation for neural networks, the core technology within AI.
Quickly following, in 1950, Alan Turing published "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," introducing the concept of the Turing Test to assess machine intelligence.
This lead to graduate students Marvin Minsky and Dean Edmonds building the first neural net machine known as the SNARC, Frank Rosenblatt developed the Perceptron which is one of the earliest models of a neural network, and Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, one of the first chatbots to simulate a Rogerian psychotherapist between 1951 and 1969.
From 1969 until 1979 Marvin Minsky demonstrated the limitations of neural networks, which caused a temporary decline in neural network research. The first "AI winter" occurred due to reduced funding and hardware and computing limitations.

1980-2006
In the 1980's, there was a renewed interest and government funding for AI research primarily in translation and transcription.During this time, expert systems, like MYCIN, became popular because they simulated human decision-making processes in specific domains like medicine. With the 1980's revival of neural networks, David Rumelhart and John Hopfield published papers on deep learning techniques showing that computers could learn from experience
From 1987-1997, due to other socio-economic factors and the dot-com boom, a second AI winter emerged. AI research became more fragmented, with teams solving domain-specific problems across different use cases.
Starting in 1997 to about 2006, we saw significant achievements in AI including IBM's Deep Blue chess software defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov. In addition to this Judea Pearl published a book that included probability and decision theory in AI research and Geoffrey Hinton and others popularized deep learning, leading to a resurgence in neural networks. However, commercial interest remained limited.

2007-Present
From 2007 to 2018, advancement in cloud computing made computing power and AI infrastructure more accessible. It led to increasing adoption. innovation and advancement in machine learning. The advancements included a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture called AlexNet, developed by Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey Hinton winning the ImageNet competition, showcasing the power of deep learning in image recognition and Google's AlphaZero mastered the games of chess, shogi, and Go without human data, relying on self-play.
In 2022, chatbots that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) to have human-like conversations and complete tasks like OpenAI's ChatGPT became widely known for its conversational abilities, renewing AI interest and development.

AI in the future
Current artificial intelligence technologies all function within a set of pre-determined parameters. For example, AI models trained in image recognition and generation cannot build websites.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a field of theoretical AI research that attempts to create software with human-like intelligence and the ability to self-teach. The aim is for the software to perform tasks for which it is not necessarily trained or developed.
AGI is a theoretical pursuit to develop AI systems with autonomous self-control, reasonable self-understanding, and the ability to learn new skills. It can solve complex problems in settings and contexts that were not taught at its creation. AGI with human abilities remains a theoretical concept and research goal. It is one possible future of AI.

How is AI used today?
AI is everywhere today, working behind the scenes to power your favorite applications.
Artificial intelligence examples for business
Artificial intelligence has a wide range of applications. While not an exhaustive list, here are examples highlighting AI's diverse use cases for organizations.
Chatbots and smart assistants
AI-powered chatbots and smart assistants engage in more sophisticated and human-like conversations. They can understand the context and generate coherent responses for complex natural language and customer queries. They excel in customer support, virtual assistance, and content generation to provide personalized interactions. These models' continuous learning capability allows them to adapt and improve their performance over time, enhancing user experience and efficiency.
For example, Deriv, one of the world’s largest online brokers, faced challenges accessing vast amounts of data distributed across various platforms. It implemented an AI-powered assistant to retrieve and process data from multiple sources across customer support, marketing, and recruiting. With AI, Deriv reduced the time spent onboarding new hires by 45 percent and minimized recruiting task times by 50 percent.

Intelligent document processing
Intelligent document processing (IDP) translates unstructured document formats into usable data. For example, it converts business documents like emails, images, and PDFs into structured information. IDP uses AI technologies like natural language processing (NLP), deep learning, and computer vision to extract, classify, and validate data.
For example, HM Land Registry (HMLR) handles property titles for over 87 percent of England and Wales. HMLR caseworkers compare and review complex legal documents related to property transactions. The organization deployed an AI application to automate document comparison, cutting review time by 50 percent and supercharging the approval process of property transfer. For more information, read how HMLR uses Amazon Textract.

Application performance monitoring
Application performance monitoring (APM) is the process of using software tools and telemetry data to monitor the performance of business-critical applications. AI-based APM tools use historical data to predict issues before they occur. They can also resolve issues in real-time by suggesting practical solutions to your developers. This strategy keeps applications running effectively and addresses bottlenecks.
For example, Atlassian makes products to streamline teamwork and organization. Atlassian uses AI APM tools to continuously monitor applications, detect potential issues, and prioritize severity. With this function, teams can rapidly respond to ML-powered recommendations and resolve performance declines.

Predictive maintenance
AI-enhanced predictive maintenance uses large volumes of data to identify issues that could lead to downtime in operations, systems, or services. Predictive maintenance allows businesses to address potential problems before they occur, reducing downtime and preventing disruptions.
For example, Baxter uses 70 manufacturing sites worldwide and operates 24/7 to deliver medical technology. Baxter employs predictive maintenance to detect abnormal conditions in industrial equipment automatically. Users can implement effective solutions ahead of time to reduce downtime and improve operational efficiencies. To learn more, read how Baxter uses Amazon Monitron.

Medical research
Medical research uses AI to streamline processes, automate repetitive tasks, and process vast data. You can use AI technology in medical research to facilitate end-to-end pharmaceutical discovery and development, transcribe medical records, and improve time-to-market for new products.
As a real-world example, C2i Genomics uses artificial intelligence to run high-scale, customizable genomic pipelines and clinical examinations. Researchers can focus on clinical performance and method development by covering computational solutions. Engineering teams also use AI to reduce resource demands, engineering maintenance, and NRE costs. For more details, read how C2i Genomics uses AWS HealthOmics.

Benefits of artificial intelligence for business
Your organization can integrate artificial intelligence capabilities to optimize business processes, improve customer experiences, and accelerate innovation.
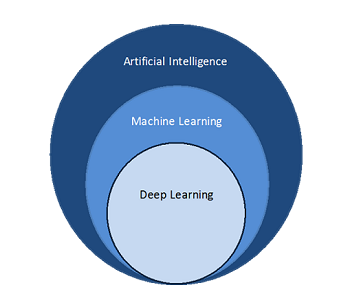
What is the difference between machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is an umbrella term for different strategies and techniques for making machines more human-like. It includes everything from self-driving cars to robotic vacuum cleaners and smart assistants like Alexa. While machine learning and deep learning fall under the AI umbrella, not all AI activities are machine learning and deep learning. For example, generative AI demonstrates human-like creative capabilities and is a very advanced form of deep learning.
Machine learning
While you may see the terms artificial intelligence and machine learning being used interchangeably in many places, machine learning is technically one among many other branches of artificial intelligence. It is the science of developing algorithms and statistical models to correlate data. Computer systems use machine learning algorithms to process large quantities of historical data and identify data patterns. In the current context, machine learning refers to a set of statistical techniques called machine learning models that you can use independently or to support other more complex AI techniques.
Deep learning
Deep learning takes machine learning one step further. Deep learning models use neural networks that work together to learn and process information. They comprise millions of software components that perform micromathematical operations on small data units to solve a larger problem. For example, they process individual pixels in an image to classify that image. Modern AI systems often combine multiple deep neural networks to perform complex tasks like writing poems or creating images from text prompts.

How does artificial intelligence work?
Artificial intelligence systems use a range of technologies to work. The specifics vary, but core principles remain the same: they convert all data types, such as text, images, videos, and audio, into numerical representations and mathematically identify patterns and relationships between them. Hence, artificial intelligence technologies require training - they are exposed to large volumes of existing datasets to "learn" — similar to humans learning from existing knowledge archives. Some of the technologies that make artificial intelligence work are given below.
Neural networks
Artificial neural networks form the core of artificial intelligence technologies. They mirror the processing that happens in the human brain. A brain contains millions of neurons that process and analyze information. An artificial neural network uses artificial neurons that process information together. Each artificial neuron, or node, uses mathematical calculations to process information and solve complex problems.
Natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) uses neural networks to interpret, understand, and gather meaning from text data. It uses various computing techniques that specialize in decoding and comprehending human language. These techniques allow machines to process words, grammar syntax, and word combinations to process human text and even generate new text. Natural language processing is critical in summarizing documents chatbots, and conducting sentiment analysis.

Computer vision
Computer vision uses deep learning techniques to extract information and insights from videos and images. You can use it to monitor online content for inappropriate images, recognize faces, and classify image details. It is critical in self-driving cars and trucks to monitor the environment and make split-second decisions.

Speech recognition
Speech recognition software uses deep learning models to interpret human speech, identify words, and detect meaning. The neural networks can transcribe speech to text and indicate vocal sentiment. You can use speech recognition in technologies like virtual assistants and call center software to identify meaning and perform related tasks.

Generative AI
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that create new content and artifacts such as images, videos, text, and audio from simple text prompts. Unlike past AI, which was limited to analyzing data, generative AI leverages deep learning and massive datasets to produce high-quality, human-like creative outputs. While enabling exciting creative applications, concerns around bias, harmful content, and intellectual property exist. Overall, generative AI represents a major evolution in AI capabilities to generate human language and new content and artifacts in a human-like manner.

What are the key components of AI application architecture?
Artificial intelligence architecture consists of three core layers. All the layers run on IT infrastructure providing the necessary compute and memory resources for the AI.
AI training options for beginners
AI training typically starts with the basics of programming and computer science. You should learn languages like Python, along with mathematics, statistics, and linear algebra.
You can then move on to more specialized training. Pursue a master’s degree in artificial intelligence, machine learning, or data science to gain a deeper understanding and hands-on experience. These programs typically involve topics such as neural networks, natural language processing, and computer vision in-depth.
However, formal education isn’t the only path. You can use online courses to learn at your own pace and master specific skills. For example, generative AI training on AWS includes certifications by AWS experts on topics like:
What are the challenges in artificial intelligence implementation?
Several challenges complicate AI implementation and usage. The following roadblocks are some of the most common challenges.
AI governance
Data governance policies must abide by regulatory restrictions and privacy laws. To implement AI, you must manage data quality, privacy, and security. You are accountable for customer data and privacy protection. To manage data security, your organization should understand how AI models use and interact with customer data across each layer.

Responsible AI
Responsible AI is AI development that considers the social and environmental impact of the AI system at scale. As with any new technology, artificial intelligence systems have a transformative effect on users, society, and the environment. Responsible AI requires enhancing the positive impact and prioritizing fairness and transparency regarding how AI is developed and used. It ensures that AI innovations and data-driven decisions avoid infringing on civil liberties and human rights. Organizations find building responsible AI challenging while remaining competitive in the rapidly advancing AI space.

Data limitations
You need to input vast volumes of data to train unbiased AI systems. You must have sufficient storage capacity to handle and process the training data. Equally, you must have effective management and data quality processes in place to ensure the accuracy of the data you use for training.

Technical difficulties
Training AI with machine learning consumes vast resources. A high threshold of processing power is essential for deep learning technologies to function. You must have robust computational infrastructure to run AI applications and train your models. Processing power can be costly and limit your AI systems' scalability.

How can AWS support your artificial intelligence requirements?
AWS makes AI accessible to more people—from builders and data scientists to business analysts and students. With the most comprehensive set of AI services, tools, and resources, AWS brings deep expertise to over 100,000 customers to meet their business demands and unlock the value of their data. Customers can build and scale with AWS on a foundation of privacy, end-to-end security, and AI governance to transform at an unprecedented rate. AI on AWS includes pre-trained AI services for ready-made intelligence and AI infrastructure to maximize performance and lower costs.